
The commonly used glass varieties of building curtain walls include tempered glass, laminated glass, fireproof glass, low-emissivity coated glass (Low-E glass), sunlight control coated glass, insulating glass and vacuum glass.
1. Flat glass
Flat glass refers to soda-lime silicate glass produced by various processes. Flat glass does not belong to safety glass, and cannot be directly used for glass curtain walls, but is used as the original piece of glass deep processing for processing and manufacturing tempered glass, laminated glass and other safety glass. Non-rectangular glass plates are collectively referred to as special-shaped plate glass, such as trapezoidal, triangular, etc. Generally, the area of special-shaped glass is calculated according to the minimum external rectangular area.
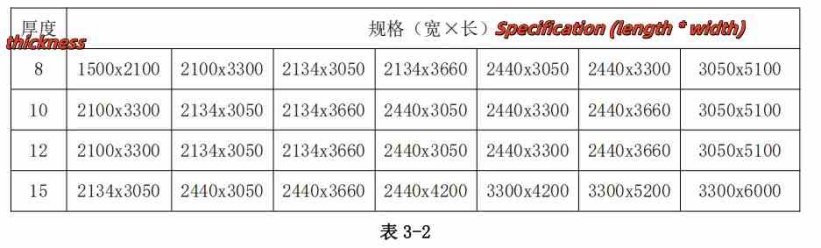
The common dimensions of the original glass sheet are as follows: Table 3-2:
2. Safety glass
Commonly used safety glass includes tempered glass, laminated glass, fireproof glass, etc.
(1) Tempered glass: tempered glass is glass after heat treatment process, which is softened after heating and cooled by cold air flow; If the tempered glass is homogenized (the second heat treatment process), it is called homogeneous tempered glass, which can greatly reduce the glass self-explosion rate. The tempered glass is characterized by the formation of a compressive stress layer on the surface of the glass, the mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance are improved, and it is granular after crushing to avoid harm to the human body.
Tempered glass is not easy to cut, and glass processing needs to be carried out before tempering. Due to the processing technology problems, tempered glass often produces stress spots and self-explosion phenomena with light and dark changes in different areas under sunlight. Many engineering cases show that the self-explosion of tempered glass has a directional distribution: generally the self-explosion probability of tempered glass in the south and west directions is large, the probability of self-explosion in the east direction is small, and the probability of self-explosion in the north direction is the smallest.
Common ways to reduce self-detonation:
a. Use the original film with less nickel sulfide stones, that is, use the original film of high quality.
b. Avoid excessive glass tempering stress.
c. Tempered glass is subjected to secondary heat treatment, which is often referred to as detonation or homogenization.
d. Ultra-clear glass. Ultra-clear glass is a type of ultra-transparent low-iron glass; In the process of iron removal and pickling in the production process, it can remove impurities such as nickel sulfide that cause glass self-explosion; Its color consistency is good, the visible light transmittance is high, the permeability is good, and the ultraviolet transmittance is low, which greatly reduces the probability of glass self-explosion. In practical engineering, ultra-clear glass is easy to identify and widely used.

(2) Laminated glass: laminated glass is a composite material that is separated by an intermediate layer and bonded by a middle layer to make it a composite material with a glass and/or plastic materials.
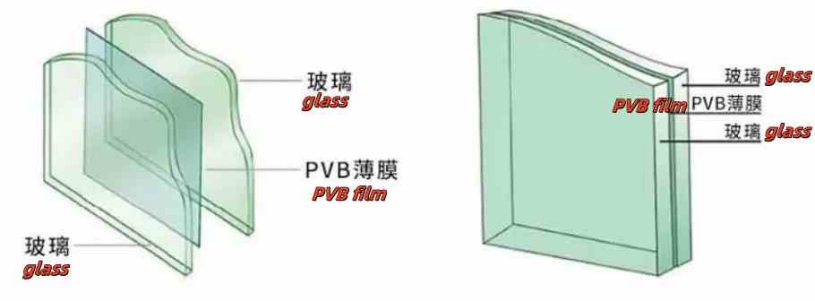
And PVB film will cause cracking of the film when exposed to water, so when using laminated glass in the project, it should be noted that the edge of the laminated glass should not be exposed to the air, otherwise the edge sealing treatment should be carried out. SGP film is 100 times harder than ordinary PVB film, and the tear strength is 5 times that of ordinary PVB film; SGP film is widely used in super high-rise buildings or oversized glass panels, and its price is more than 3-5 times that of PVB film. Generally, it is commonly used for oversized and special-shaped glass.
The thickness of the laminated glass for curtain wall should not be less than 0.76mm, and in general, when the single piece of glass is tempered glass and the thickness is 8mm, the thickness of the laminated glass should be more than 1.14mm; When the single piece of glass is tempered glass and the thickness is 10~12mm, the thickness of the laminate should be more than 1.52mm; When the single piece of glass is tempered glass and the thickness is 15mm, the thickness of the laminate should be more than 1.9mm; When the thickness of a single piece reaches more than 19mm, the thickness of the laminated film should be more than 2.28mm.
For non-tempered glass monoliths, the thickness of the laminate can be appropriately reduced, but it should not be less than 0.76mm. The following issues should be paid attention to in the process of laminated glass production and application: (1) the thickness and type of two pieces of glass should be the same as far as possible; (2) Low-E laminated glass should be placed on the outside of the inner glass (i.e., the second glass surface counted from the room).
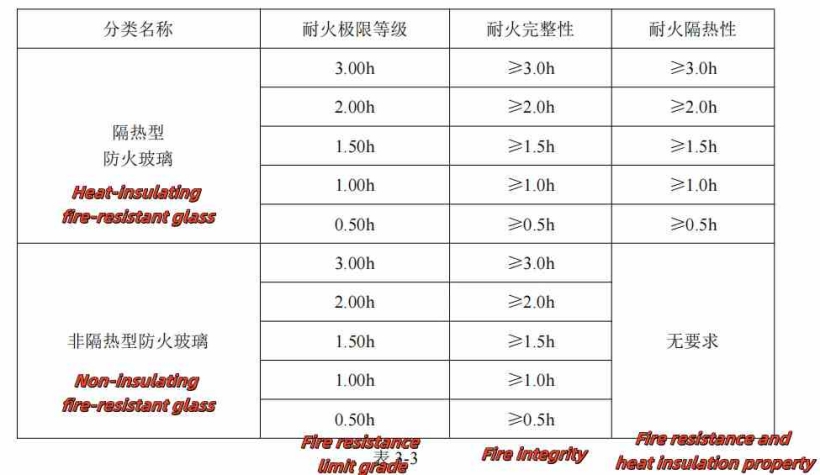
(3) Fireproof glass: fireproof glass is obtained by physical and chemical methods to treat flat glass, which is a special glass that can meet the requirements of the corresponding fire resistance. Fireproof glass can be divided into composite fireproof glass (represented by FFB) and monolithic fireproof glass (represented by DFB) according to its structure, and can be divided into heat-insulating fireproof glass (Class A) and non-heat-insulated fireproof glass (Class C) according to its fire resistance; According to the fire resistance limit, it can be divided into five grades: 0.50h, 1.00h, 1.50h, 2.00h, and 3.00h; According to the production process and its characteristics, it can be divided into dry composite fireproof glass, grouting composite fireproof glass, monolithic fireproof glass, high borosilicate fireproof glass and new silicon fireproof glass. Heat-insulating fireproof glass (FFB) and non-heat-insulating fireproof glass (DFB) shall meet the requirements of Table 3-3 below
3. Coated glass
(1) Coated glass is coated with one or more layers of metal, alloy or metal compound film on the surface of the glass to change the optical properties of the glass and meet certain special requirements. Commonly used coated glasses are sunlight control coated glass and low-emissivity coated glass (Low-E glass).
(2) Sunlight control coated glass is a typical translucent glass, which has the characteristics of one-way perspective, has a high reflection ability to sunlight, and can save air conditioning energy consumption in hot summer; It is generally used for curtain walls and lighting roofs with low thermal insulation requirements. Due to the high reflectivity of visible light, the sunlight control coated glass needs to be selected to avoid glare.
(3) Low-emissivity coated glass (high-transmittance Low-E) is also known as low-emissivity glass and "Low-E" glass, and low-emissivity coated glass can also be combined with sunlight control function, which is called sunlight control low-emissivity glass (sunshade Low-E).
(4) Single, double and triple silver Low-E glass: Low-E glass can be divided into single silver, double silver and triple silver Low-E glass according to the number of layers of silver layer.
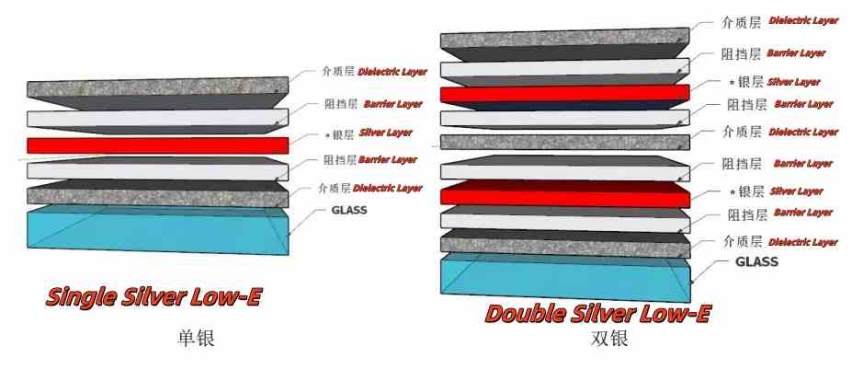
Generally, the single silver Low-E film mainly relies on the silver layer (Ag) evenly distributed in the middle layer to reflect far-infrared thermal radiation, and the thickness of the whole film layer is about 45~75nm. Silver Low-E glass alone usually contains only one functional layer (silver layer), plus other metal and compound layers, for a total of 5 layers; The silver layer (Ag) in the film layer is separated and overlapped in the middle layer, and the thickness of the silver base layer is about 5~12nm, forming a special film structure in which the metal layer and the insulating layer intersect.
Double silver Low-E glass typically has two functional layers (silver layers), plus other metal and compound layers, for a total of 9 layers; The three-silver Low-E film has three layers of silver evenly distributed among other protective metal oxides, and the three-silver Low-E glass has three functional layers (silver layers), plus other metal and compound layers, the total number of layers reaches 13 layers. Double-silver Low-E glass and triple silver Low-E glass have a lower shading coefficient and heat transfer coefficient than single-silver Low-E glass, which can block more solar radiation heat energy and filter sunlight into a cold light source to a greater extent.
When the coated glass is installed, the film side should face the indoor, and the glass side should face the outdoor; The empirical method of distinguishing between the membrane surface and the glass surface: (1) borrowing the light of a lamp or lighter to look inside the glass side, if there are two light and shadows, the light and shadow turn red is the membrane surface, and the light and shadow have no change for the glass surface; (2) Place the sharpened pencil with the tip of the pen touching the measured surface and tilting it (45~60° is appropriate), and see that the surface of the two shadows is the membrane surface, and the other side is the glass surface. (3) Observe the gluing place on the edge, because the coating side needs to be removed before the glue can be applied, and the side can be observed which side has traces of film removal, that is, the coating surface.
Fourth, insulating glass
Insulating glass is divided into flat insulating glass and curved insulating glass according to shape; According to the gas in the hollow cavity, it is divided into ordinary insulating glass (the gas in the hollow cavity is air) and insulating glass (the hollow cavity is filled with fluorine gas, nitrogen and other gases); According to the original glass sheet, it can be divided into: ordinary flat insulating glass, tempered insulating glass, sunlight control coated insulating glass, low-emissivity (Low-E) insulating glass, etc. The common configuration forms of insulating glass are ordinary insulating glass (single "air" layer) and triple glass and two-cavity insulating glass (double "air" layer).
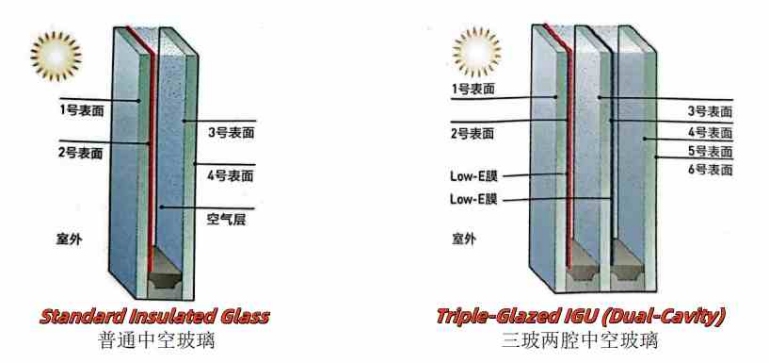
Insulating glass is characterized by excellent thermal insulation performance, thermal insulation performance, sound insulation performance, anti-condensation performance, etc. Insulating glass plays a key role in the energy saving of doors, windows and curtain walls, and at present, China's insulating glass market is more widely used as double-channel sealed aluminum spacer insulating glass. In order to improve the thermal insulation performance of insulating glass, the air cavity of insulating glass can also be filled with inert gas. The gases used for filling insulating glass are denser than air, which reduces their convection velocity and thus heat conduction.
At present, argon is the most widely used gas for insulating glass filling. Argon is a colorless, odorless, and non-toxic gas; UV-resistant, does not affect visible light transmission; With a content of 1% in the air, it is the most economical inert gas. Insulating glass is often connected by two sealants, the first sealant plays a role in preventing water vapor or inert gas from entering and exiting the cavity, generally using butyl glue, because the water vapor transmission rate and inert gas transmission rate of butyl glue are very low. However, the butyl adhesive itself has low bonding strength and small elasticity, so it is necessary to rely on two sealants to fix the overall structure, and bond the glass plate with the spacer strip together, so that when the insulating glass is under load, a sealant can maintain a good sealing effect, and the overall structure is not affected.
Insulating glass warm edge technology: In order to improve the thermal resistance around the insulating glass, it is advisable to produce condensation, and use materials with low thermal conductivity to replace the traditional aluminum spacer, so as to avoid condensation at the edge of the inner glass. At present, the warm edge partition system of insulating glass can be basically divided into two categories: one is the rigid partition system composed of metal frame and sealant with low thermal conductivity; The other type is a non-rigid spacer system made of polymer materials.

5. Vacuum glass
Vacuum glass is based on the principle of a thermos flask, which seals two pieces of glass around each other, draws the gap into a vacuum and seals the exhaust port. The gap between the two pieces of glass is 0.1~0.2mm. In order to make the glass withstand the action of atmospheric pressure in a vacuum, a support is placed between the two glass plates, and the support is very small and does not affect the light transmittance of the glass. Vacuum glass can be combined with another piece of glass, or vacuum glass with vacuum glass to form insulating glass. Its heat transfer coefficient can reach 0.5W/(m2· K) below. Vacuum glass can also be combined with tempering, laminating, wire clamping, mucous membrane and other technologies to form glass with fireproof, sound insulation, safety and other functions.
Vacuum glass has the following advantages:
(1) The thermal insulation performance of vacuum glass is good. Vacuum glass can insulate up to 2 times better than insulating glass;
(2) It has better anti-condensation performance. The condensation temperature is lower and there is no "internal condensation" problem;
(3) It has good sound insulation performance. Especially in the middle and low frequency bands, the sound insulation effect of vacuum glass is significantly better than that of insulating glass;
(4) Good long-term stability. Due to the use of ambient temperature and water vapor in the environment, after the use of insulating glass for a period of time, visible water vapor will be produced in the insulating glass cavity, resulting in the failure of insulating glass, while vacuum glass basically does not occur in this situation.
Name: Litong Glass
Mobile:+86 16632961602
Tel:+86 16632961602
Email:vip@litongglass.com
Add:Shahe city,Hebei,China